Physical Properties
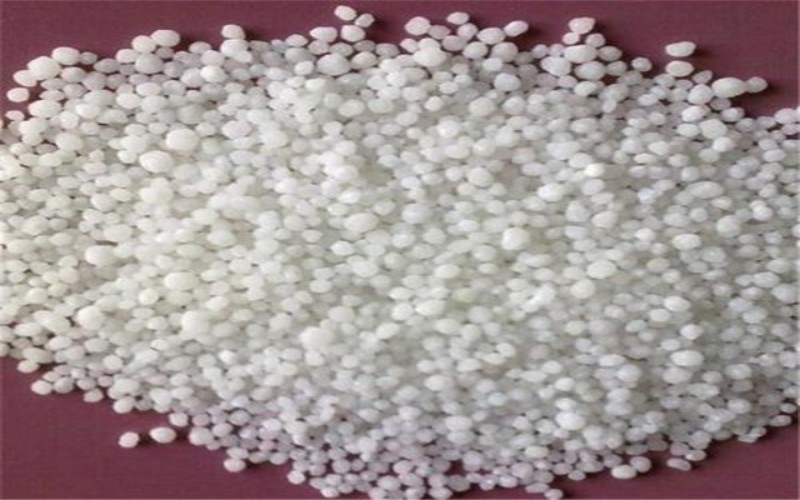
- Appearance: White or light gray granular solid; hygroscopic.
- Density: 2.50 g/cm³ (anhydrous); 1.9-1.82 g/cm³ (tetrahydrate).
- Melting Point: 561°C (anhydrous); 42.7°C (tetrahydrate hydrates melt).
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at 130-140°C.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water (121.2 g/100 mL at 20°C, 271.2 g/100 mL at 40°C); soluble in ethanol, methanol, and acetone.
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Strong oxidizer; can accelerate combustion and cause explosions when mixed with organic materials.
- Decomposition: Decomposes upon heating to form calcium oxide (CaO), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), and oxygen (O₂).Ca(NO3)2→CaO+2NO2+½O2
- Reactivity: Forms explosive mixtures with reducing agents like phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, and alkyl esters.
Uses
- Agriculture: Used as a fertilizer (provides nitrogen and calcium) and for controlling blossom-end rot in tomatoes.
- Industrial Applications:
- Used in explosives, fireworks, and matches.
- Used in the manufacture of incandescent mantles and as a corrosion inhibitor in diesel fuels.
- Used in wastewater treatment, latex production, and refrigerant manufacturing.
- Other Uses:
- Used in hydroponic culture and as a fast-acting fertilizer for acidic soils.
- Used in the production of other nitrates.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Hazards: Dust causes mild irritation to eyes; ingestion is toxic.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Strong oxidizer; contact with organic materials can cause fires or explosions.
- Storage and Handling: Store in a dry place, away from organic materials and reducing agents. Use protective equipment when handling.
Preparation
Calcium nitrate can be prepared by:
- Reacting calcium carbonate (limestone) with nitric acid:CaCO3+2HNO3→Ca(NO3)2+CO2+H2O
- Reacting calcium hydroxide with ammonium nitrate:2NH₄NO₃ + Ca(OH)₂ → Ca(NO₃)₂ + 2NH₄OH \] [^128^][^129^]
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping