| Description | Colorless to yellow liquids with a tarry odor. Flash point 178°F. Insoluble in water. Density 8.7 lb / gal. Poisonous by ingestion and skin absorption and corrosive to skin.Professions that involve dealing with the combustion of coal or wood may be exposed to higher levels of cresols than the general population. Environmental tobacco smoke is also a source of cresol exposure. Average cresol concentration may vary between the brand and type of cigarette in a 45-cubic meter chamber after six cigarettes had been smoked (ranged from 0.17 to 3.9 mg m3), although low levels of cresol can be detected in certain foods and tap water, and these do not constitute major sources of exposure for most population. Detectable levels of cresols have been reported in several consumer products including tealeaves, tomatoes, and ketchup as well as butter, oil, and various cheeses. Exposure to children occurs by the same routes that affect adults. Children are likely to be exposed to cresols through inhalation of contaminated air from automobile exhaust, waste incineration, and secondhand smoke. |
| Chemical Properties | Cresol,a clear amber to red liquid, also known as cresylic acid, methylphenol, and tricresol,is a mixture of three isomers of cresol derived from coaltar and is used in making plastics, ore flotation, refining petroleum, and as a strong antiseptic. Orthocresol is a color less solid with a melting point of 30 °C(86 OF) that is soluble in alcohol,but only slightly soluble in water. It is used in making disinfectants and as a plasticizer. Metacresol is a colorless liquid used in the manufacture of photographic developers,printing inks, and paint removers.It is also used as a leather preservative.The least soluble isomer, paracresol, is a colorless solid and is used in the production of dyes and pharmaceuticals. |
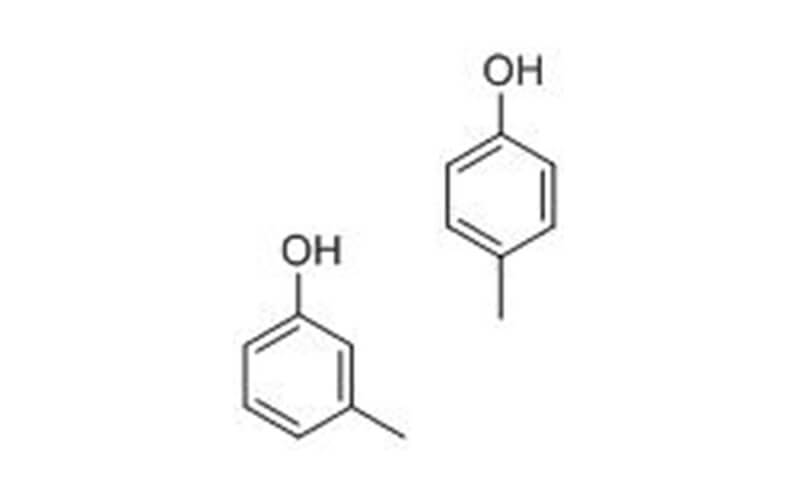
| Chemical Properties | Cresol is a mixture of the three isomeric cresols, o-, m-, and p-cresol. Cresols are slightly soluble in water. m-Isomer: Colorless or yellow liquid with characteristic odor. |
| Chemical Properties | Cresol consists of a mixture of cresol isomers, predominantly mcresol,and other phenols obtained from coaltar or petroleum.It is a colorless,yellowish to pale brownish-yellow,or pink-colored liquid, with a characteristic odor similar to phenol but more tarlike. An aqueous solution has a pungent taste. |
| Uses | Disinfectant, phenolic resins, tricresyl phosphate, ore flotation, textile scouring agent, organic intermediate, manufacture of salicylaldehyde, coumarin, and herbicides, surfactant, synthetic food flavors (para isomer only). |
| Uses | Cresol is used in disinfectants and fumigants,in the manufacture of synthetic resins, inphotographic developers and explosives. |
| Uses | Cresols (mixtures of the ortho-, meta-, and para-isomers) are synthesized by sulfonation or oxidation of toluene compounds or can be derived from coal tar and petroleum. Commercial grade crude cresol is generally a mixture of 20% o-cresol, 40% m-cresol, and 30% p-cresol. Phenol and xylenols are often found as minor contaminants. Manufacture of synthetic resins, tricresyl phosphate, salicylaldehyde, coumarin, and herbicides employ cresols. Degreasing compounds in textile scouring, paintbrush cleaners as well as fumigants in photographic developers, and explosives contains cresols. Cresols are also often used as antiseptics, disinfectants, and antiparasitic agents in veterinary medicine. Estimated breakdown of cresol and cresylic acid use is 20% phenolic resins, 20% wire enamel solvents, 10% agricultural chemicals, 5% phosphate esters, 5% disinfectants and cleaning compounds, 5% ore flotation, and 25% miscellaneous purposes. Overall, use of cresols as antimicrobial outweighs any other property. |