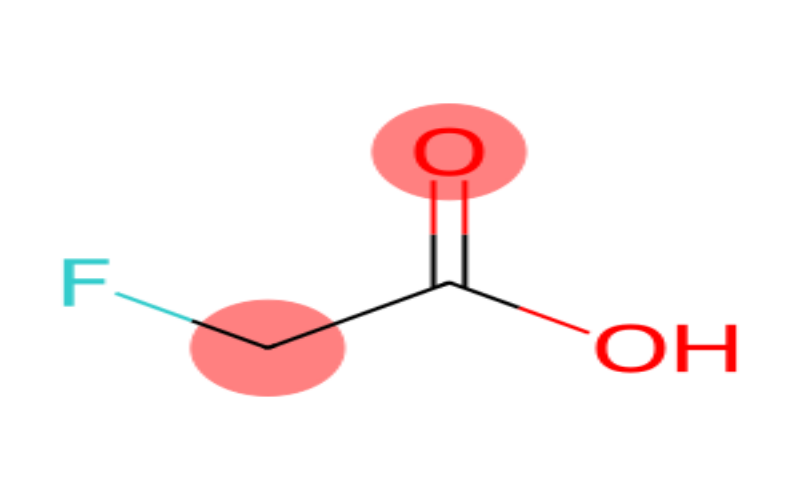
Physical Properties
- Appearance: White crystalline solid.
- Melting Point: 33°C.
- Boiling Point: 165°C.
- Density: 1.3693 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol.
- Odor: Acetic odor.
Chemical Properties
- Acidity: pKa = 2.6 (at 25°C).
- Stability: Stable in dry conditions but reacts with strong oxidizing agents.
- Metabolism: Fluoroacetic acid is metabolized to fluorocitrate, which inhibits the tricarboxylic acid cycle, leading to cellular hypoxia.
Synonyms
- 2-Fluoroacetic Acid.
- Monofluoroacetic Acid.
- Fluoroethanoic Acid.
- Gifblaar Poison.
Applications
- Pesticides: Used as a rodenticide (sodium salt) due to its high toxicity.
- Research: Used in biochemical studies to investigate metabolic pathways.
Safety Information
- Toxicity: Highly toxic; lethal dose in humans is approximately 5 mg/kg.
- Risk Phrases:
- R20/21/22: Very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin, and if swallowed.
- R35: Causes severe burns.
- R50: Very toxic to aquatic organisms.
- Safety Phrases:
- S26: In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
- S45: In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately.
Handling and Storage
- Store in a cool, dry place away from strong oxidizing agents and bases.
- Wear appropriate protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection when handling.
Environmental Concerns
- Fluoroacetic acid and its salts are highly toxic to aquatic life and should not be released into the environment.
Production Methods
- Fluoroacetic acid can be synthesized from chloroacetic acid using potassium fluoride.
- It can also be obtained by distillation of sodium fluoroacetate with sulfuric acid.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping