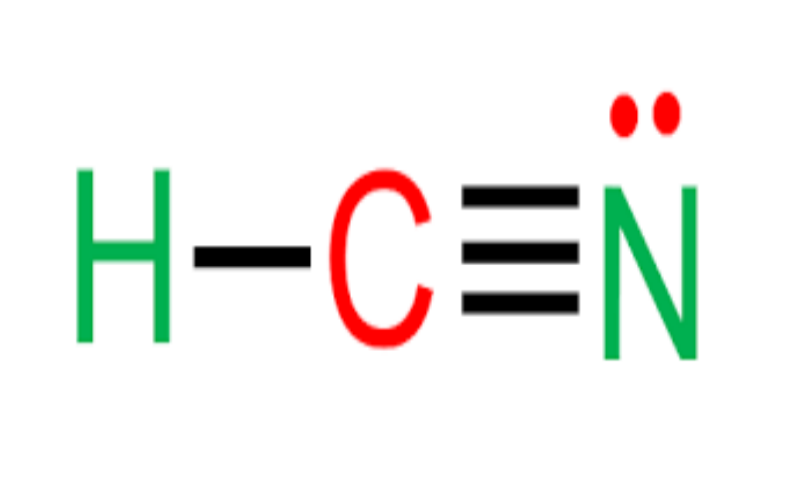Physical Properties
- Appearance: Colorless liquid or gas.
- Odor: Characteristic bitter almond odor; however, 20-60% of the population cannot detect this odor.
- Melting Point: -13.4°C.
- Boiling Point: 25.6°C.
- Density:
- Gas: 0.941 (relative to air)
- Liquid: 0.687 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Very soluble in water and ethanol; soluble in ether.
- Vapor Pressure: 750 mmHg at 25°C.
- Refractive Index: 1.2594.
Chemical Properties
- Reactivity: Highly reactive; forms explosive mixtures with air (6%-41% HCN by volume). Reacts violently with oxidizers, amines, acids, and bases.
- Decomposition: Decomposes to form hydrogen cyanide gas when heated or exposed to light.
- Acidity: Weak acid (pKa = 9.2 at 25°C).
Uses
- Industrial Applications:
- Used in the production of acrylonitrile, acrylates, cyanide salts, dyes, rodenticides, and other pesticides.
- Used as a fumigant, in electroplating, mining, and metal cleaning.
- Chemical Synthesis: Intermediate for the production of various chemicals and organic compounds.
Safety and Hazards
- Toxicity: Highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion, and skin absorption. Exposure limits:
- Ceiling: 11 mg/m³ (10 ppm) (ACGIH)
- Short-term exposure limit: 4.7 ppm (5 mg/m³) [skin] (NIOSH)
- IDLH (Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health): 50 ppm.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Forms explosive mixtures with air; autoignition temperature is 538°C.
- Storage and Handling: Store in a cool, dry place, away from oxidizers and acids. Use protective equipment when handling.
Production Methods
- Andrussow Process: Produced by the catalytic oxidation of ammonia and methane in the presence of air.
- Other Methods:
- Thermal decomposition of formamide at elevated temperatures.
- Reaction of sodium cyanide or potassium cyanide with mineral acids.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping