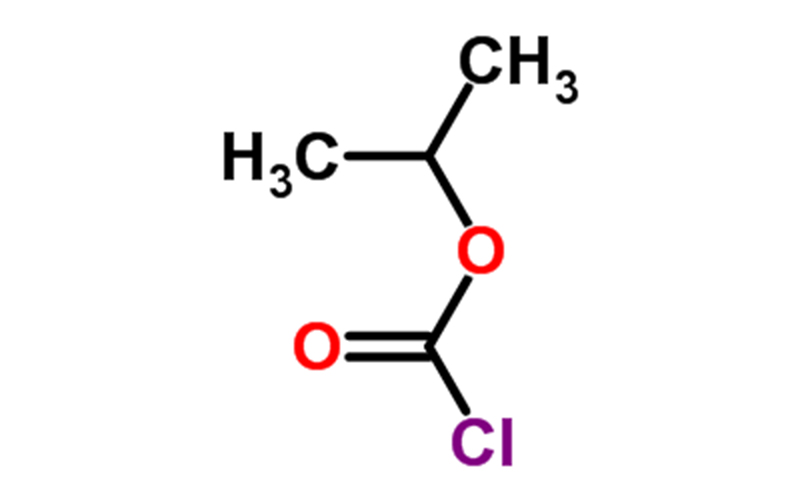
Isopropyl chloroformate Chemical Properties
| Boiling point | 105 °C |
| density | 0.892 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | 27.998hPa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.485(lit.) |
| Fp | 43 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Dichloromethane (Soluble), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Tol |
| BRN | 506416 |
| Stability: | Moisture Sensitive |
| InChIKey | IVRIRQXJSNCSPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | UN 3286 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | LQ6475000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | I |
| HS Code | 29159000 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 108-23-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |
Isopropyl chloroformate Usage And Synthesis
| Chemical Properties | Isopropyl chloroformate is a colorless liquid with corrosive properties and a pungent odor. generally present as 1.0 mol/L toluene solution of isopropyl chloroformate. It is a highly flammable chemical. Isopropyl chloroformate decomposes when heated, producing toxic and corrosive fumes, including hydrogen chloride and phosgene. The chemical reacts with water to produce alcohol and hydrogen chloride. Hydrolysis would yield chloroformic acid, which is considered a strong acid. |
| Uses | Chemical intermediate for free-radical polymerization initiators, organic synthesis. |
| Uses | Isopropyl chloroform was used in the preparation of isopropyl cyclohexane via alkylation of cyclohexene. It was also used in the preparation of 10-isopropyloctadecanoic acid via reaction with oleic acid in the presence of ethylaluminum sesquichloride |
| Production Methods | Prepared by the reaction of liquid anhydrous isopropyl alcohol with molar excess of dry, chlorine-free phosgene at low temperature. |
| General Description | A clear colorless volatile liquid with a pungent irritating odor. About the same density as water and insoluble in water. Floats on water Flash point 75°F. Very irritating to skin and eyes and very toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption. Used to make other chemicals. |
| Air & Water Reactions | Highly flammable. Gives off HCl fumes in moist air. Insoluble in water. Decomposes slowly in water forming isopropyl alcohol, HCl, and CO2. |
| Reactivity Profile | Isopropyl chloroformate is water reactive. A sample stored in a refrigerator exploded [Wischmeyer 1973]. Attacks many metals especially in humid atmosphere [Handling Chemicals Safely, 1980. p. 476]. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291]. |
| Hazard | Toxic by inhalation. |
| Health Hazard | Acute: highly toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption. Delayed: can produce delayed pulmonary edema (2-24 hours after exposure) similar to that produced by phosgene. Inhalation of material may cause death or permanent injury. |
| Fire Hazard | Extremely dangerous; Isopropyl chloroformate has exploded while stored in refrigerator. Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Like other chlorides, when heated to decomposition or on contact with acids or acrid fumes, they evolve highly toxic chloride fumes. Reacts violently with phosgene. Unstable, avoid phosgene |
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping