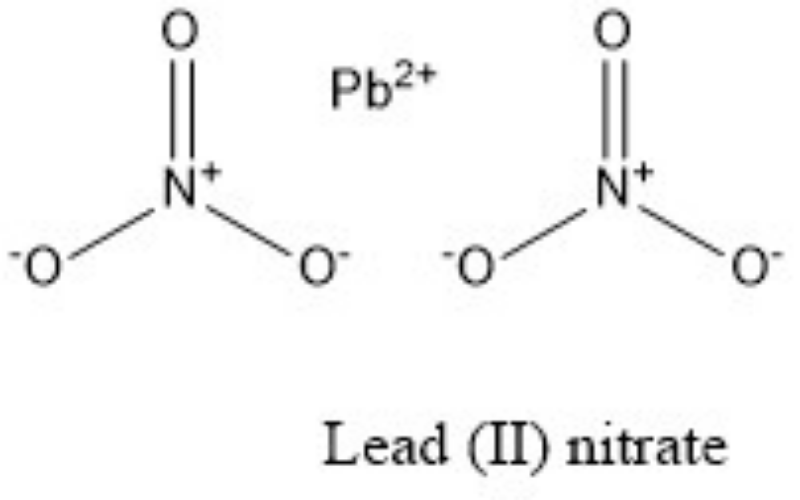
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Colorless to white crystalline powder or cubic/monoclinic crystals.
- Density: 4.53 g/cm³ at 20°C.
- Melting Point: 470°C (decomposes).
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at 500°C.
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water (486 g/L at 20°C), slightly soluble in ethanol.
- pH: 3-4 (50 g/L in water, 20°C).
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Strong oxidizer; accelerates combustion and can cause explosions when mixed with organic materials or reducing agents.
- Decomposition: Decomposes to lead oxide, nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), and oxygen when heated above 470°C.
- Reactivity: Forms explosive mixtures with reducing agents like phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, and powdered metals.
Uses
- Mining and Metallurgy: Used as an activator in flotation processes and in gold cyanidation.
- Explosives Industry: Used as an oxidizer in industrial detonators.
- Pigment Production: Used in manufacturing lead-based pigments.
- Chemical Reagent: Used in qualitative and quantitative analysis.
- Heat Stabilizers: Used in PVC and other plastics.
- Textile Industry: Acts as a mordant for dyes.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Risks: Highly toxic; prolonged exposure can cause lead poisoning, affecting the nervous system and kidneys.
- Environmental Impact: Can contaminate water and soil if improperly disposed.
- Storage and Handling: Store below 30°C, away from combustible materials and reducing agents.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Non-combustible but accelerates burning of combustible materials.
Preparation
Lead(II) nitrate is typically prepared by dissolving lead metal, lead oxide, or lead carbonate in dilute nitric acid, followed by crystallization.
Safety Information
- Classification: Oxidizing agent (Category 2).
- Self-Ignition Temperature: 400°C.
- Incompatible Materials: Combustible materials, reducing agents, powdered metals.
Lead(II) nitrate is a versatile compound with significant industrial applications, but its toxicity and strong oxidizing properties require careful handling and storage to ensure safety.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping