Product attributes
| Melting point | >900°C |
| density | 1.66 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 1.66 |
| color | Yellow |
| Water Solubility | soluble in water and ethanol |
| Crystal Structure | Reverse CaF2 type |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| crystal system | Cube |
| Space group | Fm3m |
| Lattice constant | a/nmb/nmc/nmα/oβ/oγ/oV/nm30.57180.57180.57189090900.187 |
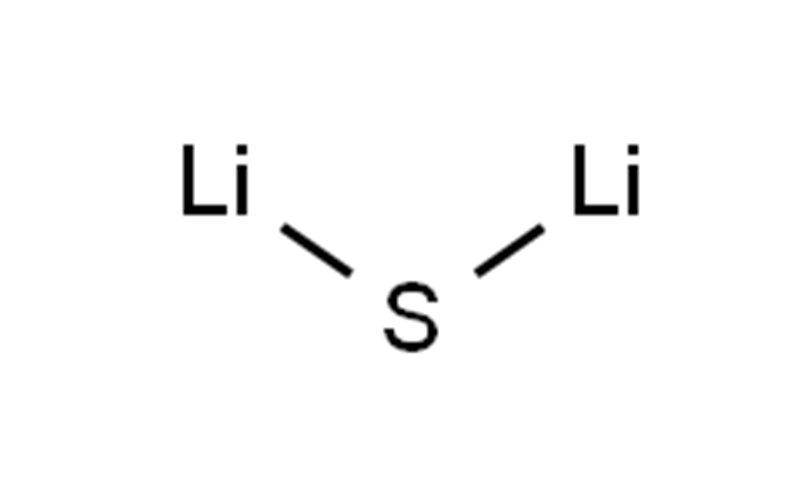
| InChI | InChI=1S/2Li.S |
| InChIKey | ZWDBUTFCWLVLCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | S([Li])[Li] |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | UN 2923 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | OJ6439500 |
| TSCA | Yes |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| Packing Group | II |
Lithium sulfide Usage And Synthesis
| Chemical Properties | Lithium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula Li2S. It crystallizes in the antifluorite motif, described as the salt (Li+)2S2−. It forms a solid yellow-white deliquescent powder. In air, it easily hydrolyses to release hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg odor) Lithium sulfide is prepared by treating lithium with sulfur. This reaction is conveniently conducted in anhydrous ammonia. The THF-soluble triethylborane adduct of lithium sulfide can be generated using superhydride. Lithium sulfide (Li2S) is considered the promising cathode material for its high theoretical capacity, high melting point, affordable volume expansion, and lithium composition. |
| Physical properties | Lithium Sulfide, Li2S, is an anti-fluorite semiconductor with a band-gap of 3.865 eV. It also has exactly the same valence electron count, Ne, and atomic number, Z, as magnesium diboride, MgB2. Both have almost the same formula weight. This qualifies Li2S as a magnesium-diboride like material. Li2S passes the same computational material specific test for superconductivity as MgB2. Lithium sulfide is a much studied material, though never tested for superconductivity. Li2S can exist in two forms: orthorhombic and cubic. The orthorhombic form belongs to space group Pmnb and has dimensions: a = 3.808Å; b = 6.311Å; c = 7.262Å. It has density of 1.75g/cm3 . The cubic version has density of 1.63g/ cm3, belongs to space group Fm-3m and has cubic dimensions 4.046Å. The electronic structure and density of states indicate that cubic Li2S is an indirect band-gap semiconductor with a band gap of 3.865 eV. Lithium sulfide melts between 900 – 975 degrees centigrade. |
| Uses | Lithium sulfide has been studied as a MgB2- like superconductor. It is also used as a cathode material in rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries. |
| Uses | Lithium sulfide (Li2S) is a product specially designed for the use in high performance batteries which can be either applied as electrode material or as precursor for solid electrolytes. It as an electrode material not only has high capacity but also overcomes many problems caused by pure sulfur electrodes. Lithium sulfide is an anti fluorite semiconductor (bandgap 3.865eV). It exists in orthorhombic and cubic structures. The densities of the orthorhombic and cubic structures are 1.75g/cm3 and 1.63g/cm3 respectively. Lithium sulfide has been studied as a MgB2- like superconductor. It is also used as a cathode material in rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries. |
| Preparation | Lithium sulfide, Li2S, is formed in the reaction of lithium with sulfur in liquid ammonia, by the decomposition of the ethanol adduct of lithium hydrogen sulfide with lithium ethanolate, and, more recently, by the reaction of hydrogen sulfide with lithium amylate to yield lithium hydrogen sulfide, LiSH, which is thermally decomposed in a vacuum to yield the sulfide. A very high quality anhydrous lithium sulfide may be prepared by the reaction of lithium metal and hydrogen sulfide in tetrahydrofuran if care is taken to exclude water. The reaction product is filtered from the reaction medium, and it is vacuum dried to remove tetrahydrofuran and to decompose the small amount of lithium hydrogen sulfide which forms. Lithium sulfide is reported to have an antifluorite structure. Lithium sulfide is readily hydrolyzed, even by water in the air, yielding hydrogen sulfide. The sulfide also reacts with sulfur to form a variety of polysulfides. |
| General Description | Lithium sulfide is an anti fluorite semiconductor (bandgap 3.865eV). It exists in orthorhombic and cubic structures. The densities of the orthorhombic and cubic structures are 1.75g/cm3 and 1.63g/cm3 respectively. |
| Toxicology | Large doses of lithium ion have caused dizziness and prostration, and can cause kidney damage if sodium intake is limited. Dehydration, weight loss, dermatological effects, and thyroid disturbances have been reported. Central nervous system effects that include slurred speech, blurred vision, sensory loss, ataxia, and convulsions may occur. Diarrhea, vomiting, and neuromuscular effects such as tremor, clonus, and hyperactive reflexes may occur as a result of repeated exposure to lithium ion. |
| Production method | Directly combine the elements, that is, mix stoichiometric lithium and sulfur, heat them in a nickel crucible under an inert atmosphere (argon or helium) until they are melted, and wait until a uniform melt is formed. Lithium sulfate can also be reduced with carbon powder. Take a mixture of 100g lithium sulfate and 436g carbon powder, and heat it in an electric furnace until a uniform melt is formed. This product is very soluble in water, and lithium hydroxide and lithium hydrosulfide are formed in the aqueous solution, which is strongly alkaline: Li2S+H2OLiOH+LiHSHydrochloric acid and lithium sulfide react rapidly when cold to produce hydrogen sulfide and lithium chloride: Li2S+HClLiCl+2H2S |
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping