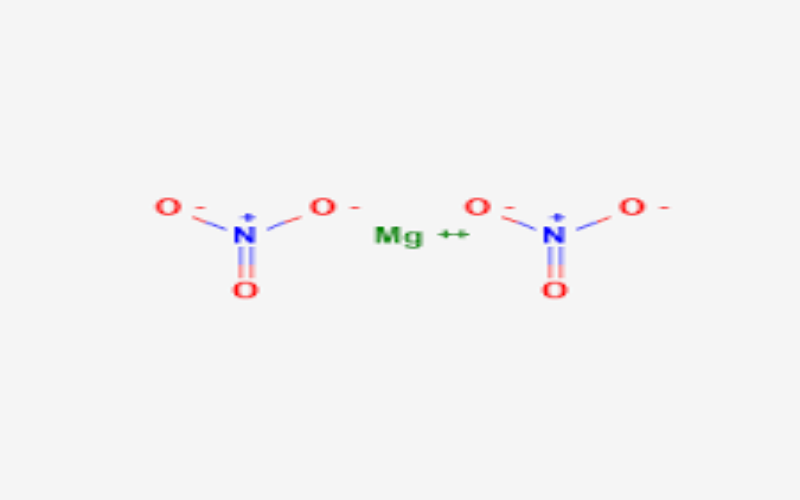
Physical Properties
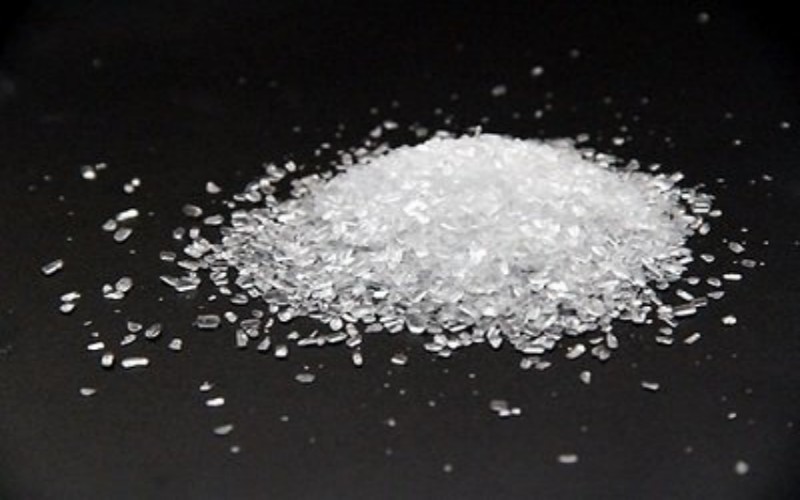
- Appearance: White crystalline solid; hygroscopic .
- Density:
- Anhydrous: 2.3 g/cm³ .
- Dihydrate: 1.45 g/cm³.
- Hexahydrate: 1.46 g/cm³.
- Melting Point:
- Anhydrous: 129°C.
- Hexahydrate: Decomposes at about 100°C.
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at 330°C.
- Solubility: Very soluble in water and moderately soluble in ethanol .
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Strong oxidizer; can accelerate combustion and cause explosions when mixed with organic materials or reducing agents .
- Decomposition:
- Anhydrous Mg(NO₃)₂ decomposes to form magnesium oxide (MgO) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) when heated.
- Hexahydrate decomposes to form basic nitrates, which further decompose at 400°C to form MgO and nitrogen oxides.
- Reactivity: Forms explosive mixtures with reducing agents like phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, and alkyl esters.
Uses
- Pyrotechnics: Used in fireworks and explosives .
- Concentration of Nitric Acid: Used to remove water and concentrate nitric acid vapors to 90-95% HNO₃.
- Agriculture: Used as a nitrogenous fertilizer with 10.5% nitrogen and 9.4% magnesium.
- Analytical Chemistry: Used as an analytical standard for magnesium and a matrix modifier in atomic absorption spectroscopy.
- Other Applications: Used in the production of ammonium nitrate, as a desensitizer for lithographic plates, and in the purification of nitric acid.
Preparation
Magnesium nitrate can be prepared by reacting nitric acid with magnesium carbonate, oxide, or hydroxide:
- MgCO₃ + 2HNO₃ → Mg(NO₃)₂ + CO₂ + H₂O .
- Mg(OH)₂ + 2HNO₃ → Mg(NO₃)₂ + 2H₂O .
Safety and Hazards
- Health Risks: Causes mild irritation to mucous membranes; ingestion may cause dizziness, abdominal pain, vomiting, and convulsions .
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Strong oxidizer; contact with organic materials or reducing agents can cause fires or explosions .
- Storage and Handling: Store in a cool, well-ventilated area, away from combustible materials and reducing agents.
Environmental Considerations
- Toxicity: Decomposition produces toxic nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) fumes.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local regulations to avoid environmental contamination.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping