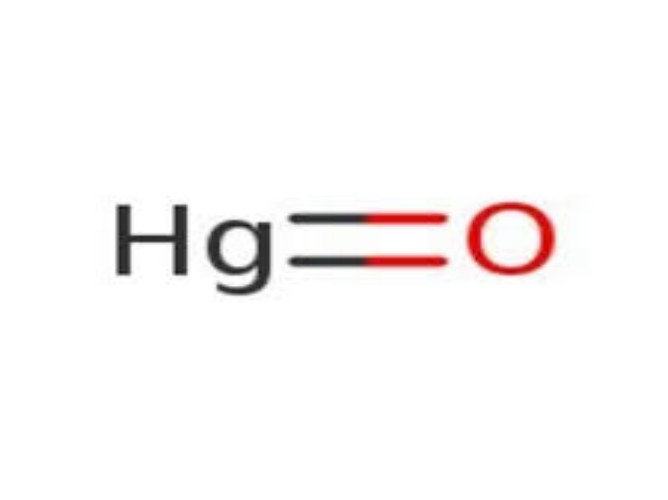
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Yellow to orange powder
- Solubility: Insoluble in water, alcohol, ether, and ammonia; soluble in acids
- Stability: Stable but sensitive to light
Preparation
Mercury oxide can be prepared through several methods:
- Thermal Decomposition of Mercury Nitrate: Heating mercury nitrate produces mercury oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen.
- Direct Oxidation: Mercury can be oxidized in air at room temperature, although this process is relatively slow.
Applications
Despite its toxicity, mercury oxide has several industrial applications:
- Battery Production: Used in mercury batteries (though these are now largely phased out due to environmental concerns).
- Laboratory Reagent: Used in the synthesis of other mercury compounds and as an oxidizing agent.
- Ceramics and Glass: Used to impart specific colors and properties.
- Electrochemical Reference: Used to determine standard electrode potentials.
Health and Environmental Impact
Mercury oxide is highly toxic and poses significant health risks, including damage to the kidneys and central nervous system upon prolonged exposure. It is also very toxic to aquatic life and can have long-term adverse effects on the environment.
Safety and Disposal
- Safety Measures: Avoid inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. Use protective clothing, gloves, and eye protection. Seek medical attention immediately in case of exposure.
- Disposal: Dispose of mercury oxide in accordance with local and international regulations. Avoid releasing it into the environment.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping