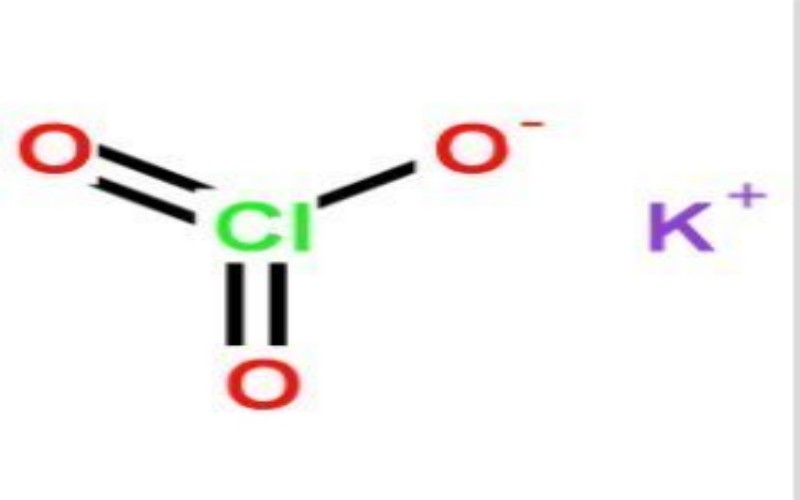
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Colorless or white crystalline powder or granules.
- Melting Point: 356-368°C.
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at around 400°C.
- Density: 2.32 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Soluble in water (73 g/L at 20°C), slightly soluble in glycerol, and insoluble in ethanol.
- pH: Neutral to slightly acidic (pH around 6-7 in aqueous solution).
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Potassium chlorate is a strong oxidizer and can decompose to release oxygen, especially in the presence of catalysts like manganese dioxide.
- Decomposition: Decomposes at high temperatures (above 400°C) to release oxygen and form potassium chloride.
- Reactivity: Forms explosive mixtures with organic materials, reducing agents, sulfur, phosphorus, and metal powders.
- Reaction with Acids: Reacts with concentrated sulfuric acid to form unstable intermediates like chloric acid and chlorine dioxide.
Preparation Methods
- Electrolytic Method: Chlorine gas is bubbled through a hot solution of potassium hydroxide to form potassium chlorate.
- Reaction: 6KOH+3Cl2→KClO3+5KCl+3H2O.
- Reactions with Chlorine: Chlorine gas can also be reacted with potassium hydroxide to produce potassium chlorate.
- Reactions with Chlorates: Chlorates like sodium chlorate can be reacted with potassium chloride to form potassium chlorate.
Uses
- Pyrotechnics and Fireworks: Used as an oxidizer in fireworks, smoke grenades, and matches.
- Laboratory Reagent: Used to generate oxygen in chemical experiments.
- Agriculture: Used as a defoliant and ripening agent for crops like cotton.
- Explosives: Used in the manufacture of explosives and rocket propellants.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Risks: Inhalation or ingestion can cause irritation, gastrointestinal issues, and methemoglobinemia.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Strong oxidizer; contact with organic materials or reducing agents can cause fires or explosions.
- Storage and Handling: Store in a cool, dry place, away from combustible materials and reducing agents. Use protective equipment when handling.
Environmental Considerations
- Toxicity: Decomposition products can be harmful to aquatic life.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local regulations to avoid environmental contamination.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping