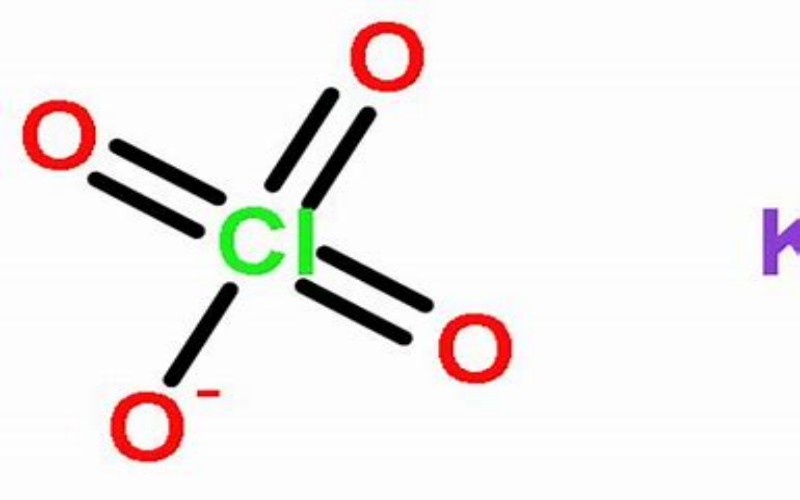
Physical Properties
- Appearance: White crystalline solid or colorless crystals.
- Density: 2.52 g/cm³.
- Melting Point: 610°C (decomposes at 400°C).
- Solubility:
- Slightly soluble in cold water (0.75 g/100 mL at 0°C).
- Soluble in boiling water (21.8 g/100 mL at 100°C).
- Practically insoluble in alcohol.
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Potassium perchlorate is a strong oxidizer and can transfer oxygen to combustible materials, greatly increasing their rate of combustion.
- Stability: Decomposes at temperatures above 400°C and may explode upon impact or when mixed with organic materials.
- Reactivity: Reacts violently with reducing agents, such as metal powders (e.g., aluminum, magnesium) and sulfur.
Uses
- Pyrotechnics and Explosives: Used in fireworks, explosive primers, ammunition percussion caps, and rocket propellants.
- Medical Use: Used as an antithyroid agent to treat hyperthyroidism.
- Analytical Chemistry: Used as an oxidizer in chemical syntheses and as a reagent in analytical chemistry.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Hazards: Inhalation, ingestion, or contact with skin or eyes can cause severe irritation, burns, or death.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Potassium perchlorate can accelerate burning and may explode when heated or contaminated with organic materials.
- Storage and Handling: Store in a cool, dry place away from combustible materials and reducing agents. Use protective equipment when handling.
Preparation
- Industrial Production: Prepared by treating an aqueous solution of sodium perchlorate with potassium chloride, exploiting the low solubility of KClO₄.
- Alternative Methods: Can also be produced by neutralizing perchloric acid with potassium hydroxide.
Environmental Considerations
- Ecotoxicity: Limited data available, but it is considered harmful to aquatic life.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local regulations to avoid environmental contamination.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping