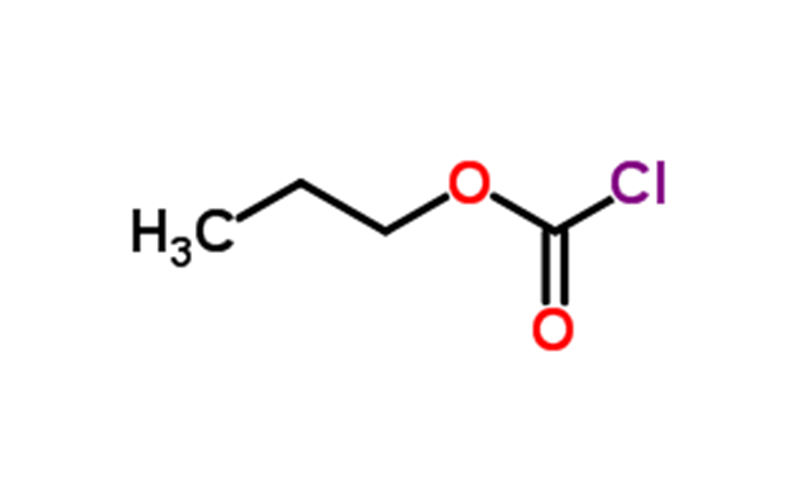
Propyl chloroformate Chemical Properties
| Boiling point | 105-106 °C(lit.) |
| density | 1.09 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.87 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.404(lit.) |
| Fp | 84 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | benzene: miscible(lit.) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Colourless |
| Specific Gravity | 1.09 |
| Melting Point | <-70ºC |
| Dielectric constant | 11.2(20℃) |
| Stability | Volatile |
| InChIKey | QQKDTTWZXHEGAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 1.385 (est) |
Safety Information
| RIDADR | UN 2740 6.1/PG 1 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | LQ6830000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | I |
| HS Code | 29151300 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 109-61-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | mouse,LC50,inhalation,319ppm/1H (319ppm),”Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology,” 3rd ed., Grayson, M., and D. Eckroth, eds. New York, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1978Vol. 4, Pg. 758, 1978. |
Propyl chloroformate Usage And Synthesis
| Chemical Properties | Propyl Chloroformate (PCF) is a colorless to yellow liquid, with a pungent odor. It reacts with water and spontaneous decomposes. It is miscible with benzene and ether. |
| Uses | Propyl Chloroformate is used as a dramatizing agent for the determination of , codeine and 6-acetyl in urine and blood using direct aqueous derivatization. |
| Application | Propyl chloroformate has been used: as derivatization reagent in quantification of dopamine, serotonin and in human urine by solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry in the preparation of dipropyl 3,6-diphenyl-1,2-dihydro-1,2,4,5-tetrazine-1,2-dicarboxylate N-propyl chloroformate is an intermediate of the fungicide propamocarb. |
| Preparation | Synthesis of Propyl chloroformate: Add n-propanol to the phosgene-passing kettle, start stirring, and then pass phosgene through the phosgene flowmeter. The phosgene-passing temperature is about 30 °C, and continue to pass the phosgene for several hours. When the end point is approached, sample and analyze, and stop when the standard is reached. Pass phosgene, cool, and then pass nitrogen to drive away phosgene and hydrogen chloride, destroy phosgene, and sample and analyze it as a product. Reaction equation: CH3CH2CH2OH+COCl2→ClCOOCH2CH2CH3 |
| Production Methods | Prepared by the reaction of liquid anhydrous n-propyl alcohol with molar excess of dry, chlorine-free phosgene at low temperature. |
| General Description | N-propyl chloroformate appears as a colorless liquid. May be decomposed by water. Severely irritates skin and eyes. Very toxic by ingestion, inhalation or skin absorption. Denser than water and vapors heavier than air. Flash point 50°F. Used to make other chemicals. |
| Air & Water Reactions | Highly flammable. Water (moisture in air or soil) reacts with generation of heat and hydrochloric acid. |
| Reactivity Profile | Unstable, decomposes spontaneously to form hydrochloric acid and other products. Avoid moist air. [EPA, 1998]. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291]. |
| Health Hazard | Strongly irritating to eyes and mucous membranes. Poisonous; may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. |
| Fire Hazard | When heated to decomposition, Propyl chloroformate emits toxic fumes of chlorine containing compounds. Propyl chloroformate is a flammable/combustible material; Propyl chloroformate may be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may travel to a source of ignition and flash back. Container may explode in heat or fire. Vapor explosion and poison hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution. Gradually decomposed by water and alcohol. Unstable, decomposes spontaneously to form hydrochloric acid and other products. Avoid moist air. |
| Flammability and Explosibility | Flammable |
| Safety Profile | Poison by skin contact. Moderately toxic by ingestion and inhalation. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame, can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. Used as a reactive intermediate to polymerization initiators. |
| Potential Exposure | Propyl chloroformate is used in organic synthesis; as an intermediate for polymerization initiators; may have been used as a military poison gas. |
| Shipping | UN2740 n-Propyl chloroformate, Hazard class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poison Inhalation Hazard, 3-Flammable liquid, 8-Corrosive material. Inhalation Hazard Zone B |
| Incompatibilities | Propyl chloroformate forms explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo- sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, water and alcohols. Reaction with water forms heat and hydrochloric acid. Attacks some metals and coating in the presence of moisture. |
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping