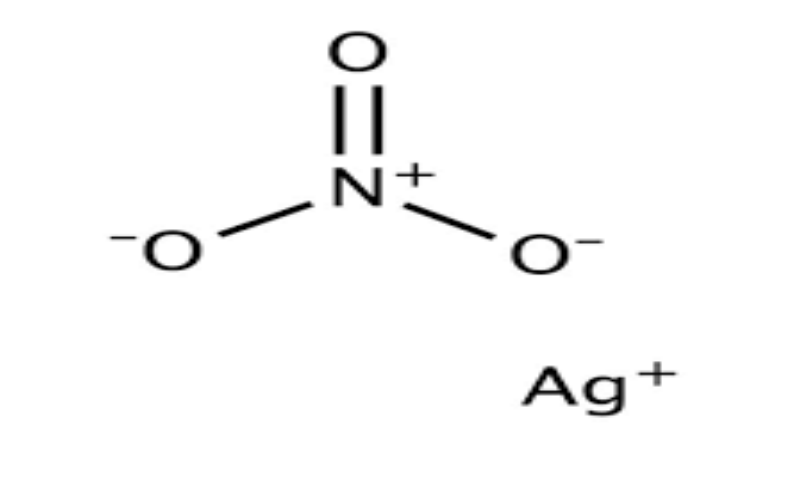
Physical Properties
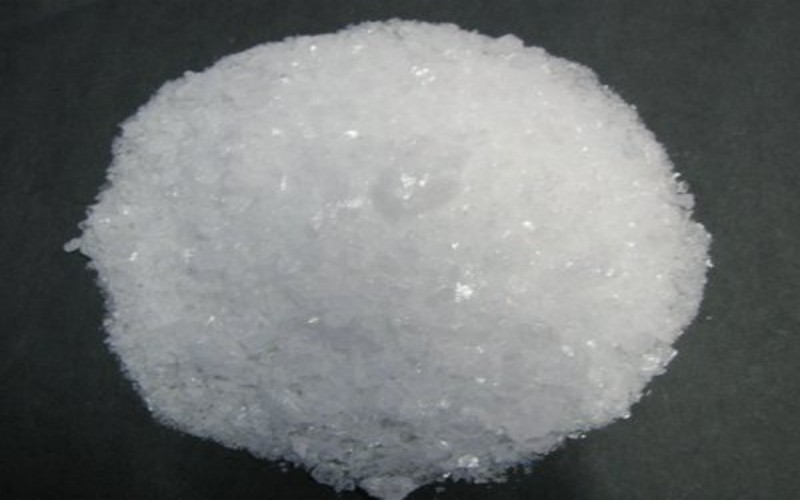
- Appearance: Colorless, transparent, orthorhombic crystals or white crystalline powder.
- Density: 4.35 g/cm³ at 20°C.
- Melting Point: 212°C.
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at 444°C to form metallic silver, nitrogen dioxide, and oxygen.
- Solubility:
- Highly soluble in water and ammonia.
- Slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in acetone, benzene, and concentrated sulfuric acid.
- pH: Aqueous solution is weakly acidic (pH = 5-6).
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Strong oxidizer that can accelerate combustion and cause explosions when mixed with organic materials or reducing agents.
- Light Sensitivity: Pure silver nitrate crystals are stable in light, but it decomposes in the presence of organic matter, turning gray or black.
- Reactions:
- Forms precipitates with halides (e.g., AgCl), sulfides (e.g., Ag₂S), and chromates (e.g., Ag₂CrO₄).
- Forms complex ions with ammonia (e.g., Ag(NH₃)₂⁺), cyanide (e.g., [Ag(CN)₂]⁻), and thiosulfate (e.g., [Ag(S₂O₃)₂]³⁻).
- Reacts with reducing agents (e.g., hydrazine, phosphorous acid) to form metallic silver.
Uses
- Photography: Used as a raw material for silver halide photosensitive materials.
- Electronics: Used in the production of conductive adhesives and silvering of electronic components.
- Medicine: Used as an antiseptic and cauterizing agent for treating warts, ulcers, and dental hypersensitivity.
- Other Applications:
- Used in mirror production, silver plating, and as an analytical reagent.
- Used in the manufacture of other silver salts and catalysts.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Risks: Strongly corrosive to skin and mucous membranes; causes irritation, ulceration, and discoloration.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Non-combustible but accelerates burning of combustible materials. Mixtures with reducing agents (e.g., phosphorus, tin(II) chloride) may explode.
- Storage and Handling: Store in a cool, dry place, away from light and organic materials. Use protective equipment when handling.
Environmental Considerations
- Toxicity: Decomposition produces toxic nitrogen oxides (NOₓ) fumes.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local regulations to avoid environmental contamination.
Preparation
Silver nitrate is typically prepared by dissolving metallic silver in dilute nitric acid, followed by evaporation and recrystallization.
- Reaction: Ag + 2HNO₃ → AgNO₃ + H₂O + NO₂↑.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping