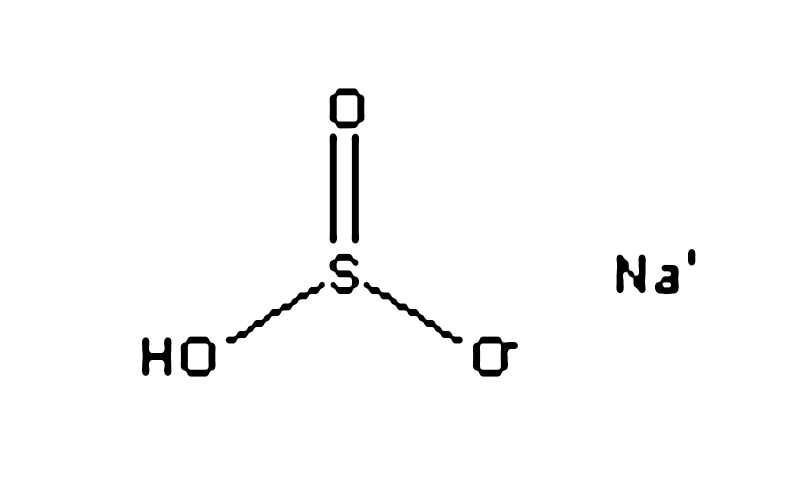
Sodium bisulfite (chemical formula: NaHSO3) is a versatile chemical raw material with the following main uses:
- 1.Reductant: In chemical experiments, sodium bisulfite is mainly used as a reductant, such as in reduction reactions in organic synthesis.
- 2.Bleaching Agent: Industrially, sodium bisulfite is used in large quantities in the dye industry and as a dechlorinating agent for bleaching fabrics. It is also used for bleaching cotton fabrics and organic substances, and in the bleaching processes of the papermaking, textile, and food processing industries.
- 3.Oxygen Scavenger: Sodium bisulfite is used as an oxygen scavenger in oilfield water injection treatment systems and is a chemical oxygen scavenger and dechlorinating agent for low-pressure boiler feed water. It is more commonly used as a chemical oxygen scavenger in medium and low-pressure boilers.
- 4.Food Additive: In the food industry, sodium bisulfite is used as a food additive to maintain the freshness of food and extend its shelf life. It can be used as a preservative and antioxidant, has a bleaching effect on food, and strongly inhibits the oxidative enzymes in plant-based foods.
- 5.Pharmaceutical Preparation: In the pharmaceutical industry, sodium bisulfite can be used to synthesize some pharmaceutical raw materials, such as drugs with certain therapeutic effects on influenza and bronchitis. It is also used in the production of metamizole and aminopyrine intermediates.
- 6.Water Treatment: Sodium bisulfite can be used in wastewater treatment to remove heavy metal ions from wastewater. It can also be used as a dechlorinating agent for wastewater, removing chlorine gas from wastewater by reacting with it.
PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Physical State; Appearance
COLOURLESS-TO-YELLOW LIQUID WITH CHARACTERISTIC ODOUR.
Chemical dangers
Decomposes on heating and on contact with acids. This produces sulfur oxides. Reacts with acids and strong oxidants. This generates fire hazard. The substance is a weak acid. Attacks metals.
EXPOSURE & HEALTH EFFECTS
| Routes of exposure The substance can be absorbed into the body by ingestion. Effects of short-term exposure The substance is irritating to the skin, eyes, respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract. Exposure could cause asthma-like reactions or urticaria in sensitive persons. | Inhalation risk No indication can be given about the rate at which a harmful concentration of this substance in the air is reached. Effects of long-term or repeated exposure Repeated or prolonged inhalation may cause asthma-like symptoms. The substance may have effects on the skin |
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping