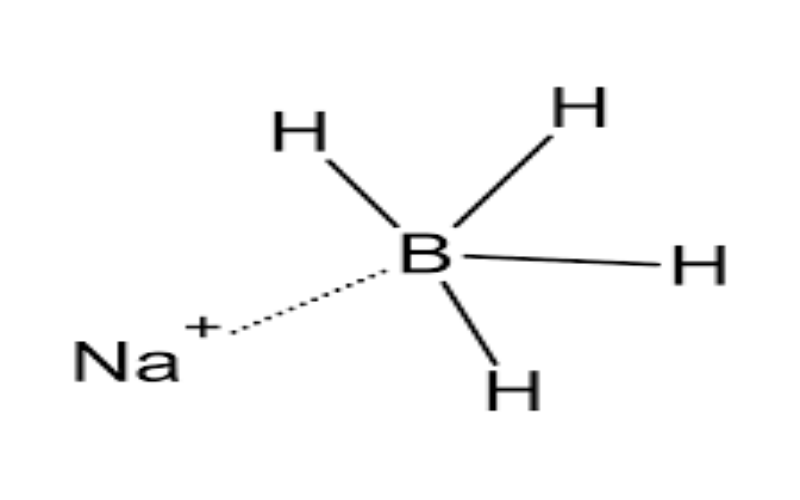
Physical Properties
- Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder.
- Density: 1.035 g/cm³ at 25°C.
- Melting Point: >300°C (decomposes).
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at 500°C.
- Solubility:
- Soluble in water (stable at pH 14, decomposes in acidic conditions).
- Soluble in methanol (13 g/100 mL) and ethanol (3.16 g/100 mL), but decomposes to borate salts.
- Slightly soluble in tetrahydrofuran and polyethylene glycol.
- Insoluble in ether, benzene, and hydrocarbons.
- Hygroscopicity: Strongly hygroscopic, easily absorbs moisture and decomposes in humid air.
Chemical Properties
- Stability: Stable in dry air and in alkaline solutions (pH 14); decomposes in acidic conditions to release hydrogen gas.
- Reduction Reactions:
- Reduces aldehydes to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols.
- Can selectively reduce carbonyl groups in the presence of other functional groups (e.g., esters, amides).
- Reacts with water to release hydrogen gas:NaBH₄ + 2H₂O → NaBO₂ + 4H₂↑ \][^156^].
- Applications as a Reducing Agent: Widely used in organic synthesis for reducing carbonyl compounds, esters, and amides under mild conditions.
Preparation
- Typically prepared by reacting sodium hydride with boron trifluoride or by reducing boric acid with sodium metal and hydrogen.
Uses
- Organic Synthesis: Used as a selective reducing agent for carbonyl compounds.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used in the synthesis of antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and cancer medications.
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Used as a bleaching agent and in the treatment of mercury-containing wastewater.
- Hydrogen Generation: Potential use in hydrogen storage and fuel cells due to its ability to release hydrogen gas upon hydrolysis.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Risks: Inhalation or skin contact can cause irritation and harm. Decomposition products (e.g., hydrogen gas) are flammable.
- Storage: Store in a dry, cool place; keep away from moisture and acidic environments. Handle in a well-ventilated area.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping