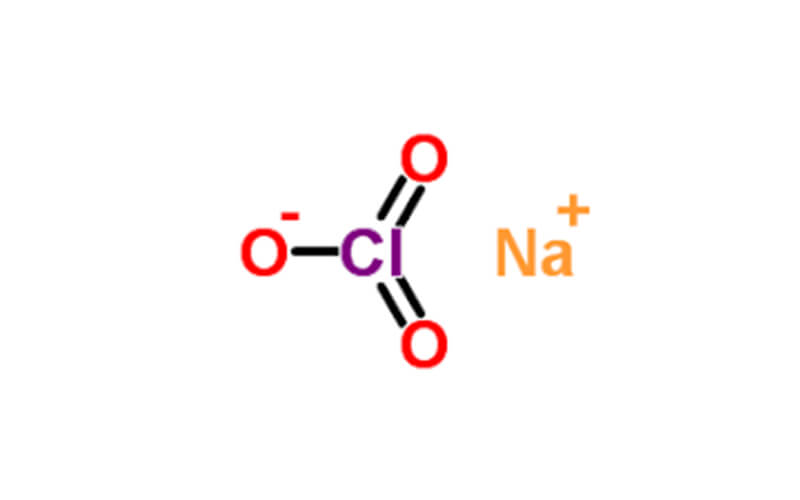
Sodium chlorate (NaClO3) is an inorganic compound with strong oxidizing properties, which makes it useful in a variety of industrial and laboratory applications:
- · Paper and Textile Industry: As a bleaching agent for pulp and textiles.
- · Water Treatment: Disinfects drinking and industrial water by producing chlorine.
- · Metal Processing: Used in cleaning and etching metals.
- · Agriculture: Acts as a herbicide to control weeds in non-crop areas.
- · Explosives and Fireworks: Used in manufacturing certain explosives and fireworks.
- · Laboratory Analysis: Serves as an analytical reagent for chemical detection.
- · Oxygen Generators: Functions as an oxidizer to produce oxygen.
- · Swimming Pools and Spas: Maintains water quality through disinfection.
- · Food Industry: Approved in some countries as a bleaching agent or preservative.
- · Battery Manufacturing: Used in certain types of batteries, including lithium batteries.
- · Medical Applications: Acts as an intermediate in some pharmaceuticals.
- · Environmental Monitoring: Determines chlorine levels in environmental samples.
PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Physical State; Appearance
HYGROSCOPIC ODOURLESS COLOURLESS-TO-WHITE CRYSTALS.
Physical dangers
No data.
Chemical dangers
Attacks zinc and steel. The substance is a strong oxidant. It reacts with combustible and reducing materials and strong acids. This generates fire and explosion hazard. Reacts with many organic materials. This produces shock-sensitive mixtures. This generates explosion hazard. Decomposes above 300°C . This produces oxygen, which increases fire hazard. This produces toxic fumes of chlorine.
EXPOSURE & HEALTH EFFECTS
| Routes of exposure The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation of its aerosol and by ingestion. Effects of short-term exposure The substance is mildly irritating to the eyes, skin and respiratory tract. The substance may cause effects on the blood. This may result in the formation of methaemoglobin. The substance may cause effects on the kidneys. This may result in kidney impairment. The effects may be delayed. See Notes. Medical observation is indicated. | Inhalation risk No indication can be given about the rate at which a harmful concentration of this substance in the air is reached. Effects of long-term or repeated exposure The substance may have effects on the thyroid. This may result in impaired functions. |
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping