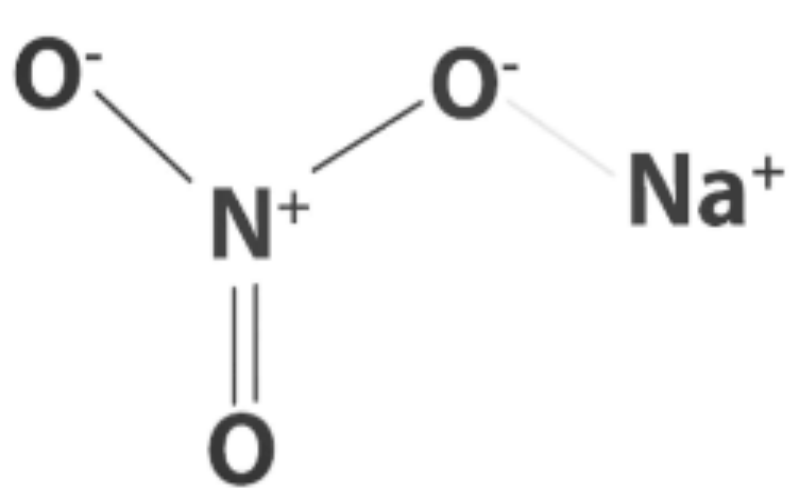
Physical Properties
- Appearance: Colorless or white crystalline solid, often granular or powder form.
- Density: 2.26 g/cm³ at 20°C.
- Melting Point: 308°C (586°F).
- Boiling Point: Decomposes at higher temperatures, releasing nitrogen oxides (NOₓ).
- Solubility:
- Soluble in water: 73 g/100 mL at 20°C.
- Slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in liquid ammonia.
Chemical Properties
- Oxidizing Agent: Sodium nitrate is a strong oxidizer and can react violently with reducing agents and organic materials.
- Stability: Stable at room temperature but decomposes at high temperatures to release toxic nitrogen oxides (NOₓ).
- Hygroscopic: It can absorb moisture from the air, forming a solution on its surface.
Uses
- Agriculture: Used as a fertilizer, providing nitrogen (16% N) and improving soil quality.
- Food Industry: Used as a preservative and color fixative in cured meats (e.g., ham, bacon) to prevent spoilage and maintain color.
- Industrial Applications:
- Used in the production of glass and ceramics as a flux.
- Used in the manufacture of explosives and pyrotechnics.
- Used in molten salt baths for heat treatment of metals.
- Medical Uses: Historically used as a diuretic and antihypertensive agent.
Safety and Hazards
- Health Hazards: Inhalation or ingestion may cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and throat. Chronic exposure can lead to methemoglobinemia and other health issues.
- Fire and Explosion Risk: Sodium nitrate is a powerful oxidizer and can accelerate combustion. It poses a significant fire and explosion risk when mixed with organic materials or reducing agents.
- Storage and Handling: Store in a cool, dry place away from organic materials and reducing agents. Use protective equipment when handling.
Environmental Considerations
- Ecotoxicity: Limited data available, but it is generally considered harmful to aquatic life.
- Disposal: Dispose of in accordance with local regulations to avoid environmental contamination.
Production Methods
- Commercial Production: Sodium nitrate is typically produced by reacting sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate with nitric acid.
- Alternative Method: It can also be obtained from natural deposits (e.g., Chile saltpeter) through extraction and purification processes.
Summary
Sodium nitrate is a versatile chemical with a wide range of applications, particularly in agriculture, food preservation, and industrial processes. However, its strong oxidizing properties require careful handling and storage to ensure safety.
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping