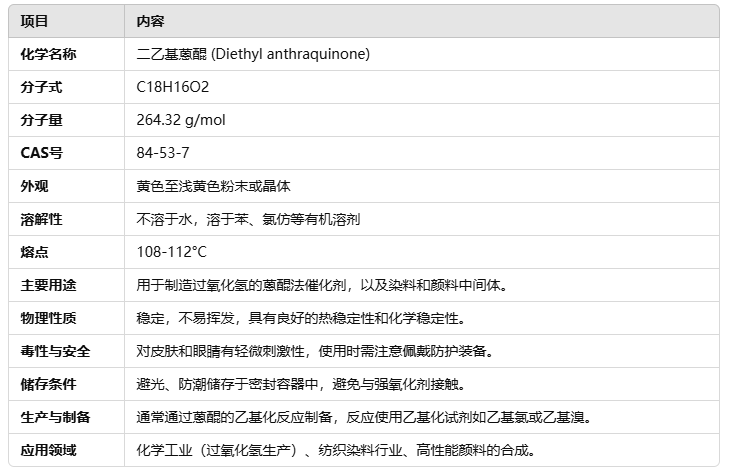
What Is 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone Used For?
2-Ethyl anthraquinone plays a key role in producing hydrogen peroxide, a widely used chemical. This organic compound serves as a crucial catalyst in the manufacturing process, making it essential for industrial applications. Its stability and efficiency make it valuable in industries like pharmaceuticals, textiles, and electronics. Understanding its purpose and significance can shed light on its impact across various fields.
Applications in Industries
2-Ethyl anthraquinone is integral to multiple industries, thanks to its chemical properties. Its versatility makes this compound vital for producing dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals. Here’s how it’s used across various fields:
Dyes and Pigments
2-Ethyl anthraquinone serves as a critical intermediate in manufacturing dyes and pigments. Its stability and reactive properties contribute to creating vibrant, long-lasting colors. These features make it ideal for producing anthraquinone-based dyes, commonly used in the textile and paper industries. Its ability to enhance dye adherence and brightness is unparalleled, ensuring high-quality results. You can explore more about its role here.
Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceuticals, 2-ethyl anthraquinone is a key player in synthesizing complex organic compounds. It acts as a precursor for medicinal product development, providing a base for creating treatments that require stable chemical structures. Chemists rely on its properties to manipulate molecular configurations for targeted drug therapies. For further details, check out this overview.
Agricultural Products
This compound also finds its place in agriculture, particularly in herbicides and pesticides. Its chemical stability ensures effectiveness in disrupting plant growth cycles and controlling pests. Manufacturers leverage its properties to develop safer, more reliable agricultural solutions. Interested in its agricultural applications? Learn more here.
These industries showcase the versatility of 2-ethyl anthraquinone, bridging science and everyday applications seamlessly.
Chemical Properties of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone
When examining 2-ethyl anthraquinone, its chemical properties reveal why it’s a highly sought-after compound in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to chemical manufacturing. Here, we’ll focus on its solubility, stability, and reactivity.
Solubility and Stability
2-Ethyl anthraquinone demonstrates selective solubility, primarily dissolving in organic solvents like chlorobenzene, toluene, and benzene. This behavior is particularly advantageous for industrial processes where controlling solvent interactions is crucial. Research shows its solubility increases with higher temperatures, which further optimizes its utility in specific manufacturing techniques. You can explore these behaviors in greater depth here.
In terms of stability, this compound stands out. It retains its structural integrity under normal storage conditions and maintains efficacy during reactions, even in elevated temperatures. However, it may degrade under prolonged exposure to strong acids or oxidizing agents. This balance of stability and selective reactivity makes it ideal for extended use in chemical processes. For additional insights, refer to this resource.
Reactivity
Chemically, 2-ethyl anthraquinone is known for its predictable and efficient reactivity. The compound readily participates in hydrogenation reactions, which is central to its role in producing hydrogen peroxide. During hydrogenation, it undergoes simultaneous reduction and regeneration, always returning to its original state. This cyclical process ensures minimal material loss, making it cost-effective.
Additionally, it undergoes aromatic substitution reactions, where the ethyl functional group provides a controlled site for interaction with other chemicals. For instance, its reactivity boosts the synthesis of other complex quinones and derivatives. Curious about more specifics? Check this comprehensive breakdown.
Through a balance of solubility, stability, and reactivity, 2-ethyl anthraquinone continues to be an indispensable material in chemical innovation. Understanding its properties is key to fully appreciating its versatility and functionality.
Safety and Handling
When working with 2-ethyl anthraquinone, following strict safety measures is critical to protect both human health and the environment. This section outlines key safety considerations related to its toxicity and the recommended personal protective equipment (PPE) for handling this chemical.
Toxicity Levels
2-ethyl anthraquinone is relatively stable but can pose risks if not handled with care. Here are some key points regarding its toxicity:
- Human Toxicity: Studies show that acute toxicity levels in humans are low, with an LD50 value exceeding 2,000 mg/kg in oral tests. However, prolonged or repeated exposure may cause organ damage. For additional safety data, check out this resource.
- Environmental Toxicity: This compound is classified as highly toxic to aquatic life. It can cause long-term detrimental effects to water-based ecosystems if released in significant quantities. Learn more about this classification and its impact here.
Understanding these risks helps mitigate harm during use and disposal, emphasizing the need for proper handling and storage practices.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper protective gear is essential for anyone handling 2-ethyl anthraquinone. Below is a list of recommended PPE to ensure safety:
- Gloves: Use disposable nitrile gloves for short-term handling or thicker chemical-resistant gloves for prolonged exposure. Explore more glove options here.
- Eye Protection: Safety goggles or face shields are mandatory to prevent contact with eyes, especially during spills or splashes.
- Clothing: Wear a chemical-resistant lab coat, full-body coveralls, or a splash-resistant suit for maximum skin coverage.
- Respirators: If working in poorly ventilated areas, use a NIOSH-approved respirator to avoid inhalation of fine particles or vapors. Check out respirator options here.
- Footwear: Closed-toe, chemical-resistant shoes ensure foot protection in the lab or industrial settings.
Employers and individuals must ensure that all PPE complies with safety standards and is checked regularly for defects. For a deeper dive into PPE options for chemical handling, refer to this guide.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can maintain a safer workspace while minimizing health and environmental risks.
Future Trends
The future of 2-ethyl anthraquinone looks promising as research explores innovative uses and expanded applications. While its roles in existing industries are well-defined, there’s untapped potential for this compound that could redefine its impact on modern science and industry.
Innovations in Applications
Emerging research is unlocking the possibilities for 2-ethyl anthraquinone beyond its current uses. What else might this compound achieve in the coming years? Scientists are exploring its role as a precursor in new catalytic systems, aiming to optimize industrial processes while reducing costs.
Some potential areas of development include:
- Advanced Catalysts: Innovations in catalytic hydrogenation processes could improve the efficiency and sustainability of hydrogen peroxide production. This is outlined in research noted here.
- Sustainability in Manufacturing: With growing interest in green chemistry, adapting 2-ethyl anthraquinone for eco-friendly industrial processes is a major focus. This includes biodegradable derivatives and safer reaction pathways.
- Nanotechnology Applications: Researchers are exploring its potential in creating nanoscale materials, which could revolutionize applications in medical imaging or advanced electronics.
Global market forecasts suggest a steady annual growth rate for 2-ethyl anthraquinone, supporting its expanded role in various fields. For more insights into market trends, visit this report.
Environmental Impact
As industries emphasize sustainability, assessing the environmental footprint of chemicals like 2-ethyl anthraquinone becomes critical. Although valued for its stability and reactivity, it carries environmental risks that must be addressed responsibly.
Key environmental concerns include:
- Toxicity to Aquatic Life: The compound’s high toxicity to aquatic organisms necessitates stringent disposal methods to prevent water contamination. Learn more from ECHA’s findings.
- Emission Control: Manufacturing processes involving 2-ethyl anthraquinone must tackle emission-related pollutants. Improvements in cleaner technologies are vital for reducing its impact.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Globally, regulations are tightening to ensure environmental safety. Companies must comply with these standards or explore sustainable alternatives to remain viable.
Forward-thinking efforts in green chemistry and stricter handling protocols can mitigate these effects. Even as industries push for progress, balancing innovation with environmental responsibility remains a key challenge. For detailed coverage on its classification and guidelines, refer to this source.
Looking ahead, tackling these environmental hurdles while pushing the boundaries of its applications is where 2-ethyl anthraquinone’s true potential lies.



