what is toluene diisocyanate
Chemical Structure and Properties of Toluene Diisocyanate
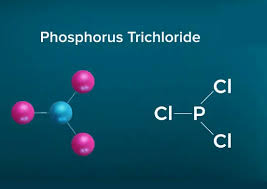
TDI is a chemical compound that belongs to the diisocyanate family. Its chemical formula is C9H6N2O2, and it consists of a toluene backbone with two isocyanate (-NCO) groups. These isocyanate groups are responsible for TDI’s high reactivity, allowing it to bond efficiently with other materials like alcohols. This makes it a key ingredient in the production of polyurethanes.
There are two isomers of TDI mainly used in industrial applications: 2,4-toluene diisocyanate and 2,6-toluene diisocyanate. Typically, commercial TDI mixtures contain 80% of the 2,4-isomer and 20% of the 2,6-isomer. These isomers differ slightly in their structures, which impacts their reactivity and the properties they impart to finished products.
In its pure form, TDI is a clear, pale yellow liquid with a sharp, pungent odor that isn’t easily missed. Its liquid state simplifies storage and transportation, but its high reactivity demands careful handling to ensure safety.
Key Applications of Toluene Diisocyanate
TDI’s versatility shines through in its numerous applications. Manufacturers rely heavily on it to produce polyurethanes, which are found in many products we interact with daily. These applications include:
- Flexible Foams: TDI is a critical ingredient in creating polyurethane foam. It’s used in furniture cushions, mattresses, and automotive seating. The foam’s flexibility and long-lasting durability come directly from its chemical properties.
- Coatings: TDI is essential for producing protective polyurethane coatings. These coatings are used across industries to provide surface protection on items like floors, machinery, and vehicles.
- Adhesives and Sealants: TDI’s bond-forming ability makes it a popular choice in adhesives and sealants. These are widely used in construction and manufacturing to create strong, durable connections between materials.
- Elastomers: TDI helps create polyurethane elastomers, which are rubber-like materials used in rollers, belts, and seals. Their ability to handle stress and return to shape makes them indispensable in many industries.
The broad scope of products created with TDI highlights just how integral it is to modern production processes. Its unique properties make it a go-to chemical for manufacturers aiming to enhance the performance and longevity of their products.
TDI in Polyurethane Production
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) plays a central role in the production of polyurethanes, materials that dominate industries from construction to consumer goods. Its chemical properties make it an indispensable building block for creating both flexible and rigid polyurethane products. Let’s examine how TDI contributes to these applications.
Flexible Foams
TDI serves as a primary component in the manufacture of flexible polyurethane foam, something you probably encounter every day. Think about that sofa cushion or your bed mattress. These products rely on TDI for their ability to contour to pressure and bounce back over time. Here’s what makes TDI ideal:
- Lightweight yet durable: Flexible foam made with TDI maintains its shape while offering comfort for years.
- Wide usage: It’s heavily used in furniture, car seats, and even footwear.
- Customizable density: Manufacturers adjust the formulations to meet each product’s needs, whether for softness or firmness.
Without TDI, everyday comforts like restful sleep and ergonomic seating would lose their edge.
Rigid Foams
For applications where strength and insulation are priority, rigid polyurethane foams crafted with TDI come into play. These foams serve as insulation panels in buildings, refrigeration units, and even industrial pipelines. Let’s outline why TDI is crucial here:
- Thermal insulation: It helps in producing foams that effectively minimize heat transfer, leading to energy efficiency.
- Structural integrity: Rigid foams maintain high compressive strength, ensuring stability in construction materials.
- Moisture resistance: Products made with TDI-based rigid foam resist water infiltration, adding longevity.
TDI ensures that homes stay warm, energy bills stay low, and structures remain reliable.
Other Polyurethane Products
Beyond foam, TDI contributes to a range of other polyurethane innovations. Its versatility supports products that face heavy use and wear, like:
- Coatings: Polyurethane coatings derived from TDI protect surfaces from scratches, chemicals, and corrosion.
- Elastomers: These are rubber-like materials used in wheels, conveyor belts, and industrial rollers.
- Adhesives and Sealants: TDI-based polyurethanes create durable bonds, ensuring materials hold together under tough conditions.
These products are designed to last, showcasing TDI’s reliability and versatility in manufacturing.
Whether it’s the comfort of a foam mattress, the insulation in your walls, or the durability of industrial coatings, TDI remains a cornerstone in polyurethane production. It’s the invisible helper behind so many products we depend on daily.
Regulatory Actions and Safety Guidelines
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI), while essential in industrial applications, requires strict handling due to its potential health risks. Regulatory bodies and safety protocols ensure proper use to protect workers, consumers, and the environment.
EPA Significant New Use Rule (SNUR)
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) closely regulates TDI usage to mitigate risks. Under the Significant New Use Rule (SNUR), specific notification requirements exist for companies introducing new uses of TDI. This rule ensures adequate oversight and safety.
- Notification Requirements: Any company planning new manufacturing or processing practices involving TDI must notify the EPA at least 90 days in advance. This allows the agency to evaluate potential risks and prevent hazardous exposure.
- Safety Thresholds: The SNUR outlines specific exposure thresholds, particularly for high-concentration use of TDI. Once airborne TDI levels reach a programmed limit, additional measures must be implemented to minimize risks. These include enhanced ventilation and restricted worker access.
For more details about TDI risk management, you can refer to the EPA’s official guidance on diisocyanates.

Safety Measures for Workers and Consumers
Protecting workers who handle TDI and consumers exposed to its residues is a priority. Here are crucial safety practices:
For Industrial Workers:
- Wear Proper Protective Equipment (PPE): Always use gloves, goggles, and respiratory gear. This minimizes direct skin or inhalation exposure.
- Monitor Air Quality: Install air monitoring systems to detect TDI levels and enhance ventilation in confined spaces.
- Follow Proper Handling Procedures:
- Store TDI in sealed containers away from moisture and heat sources.
- Employ closed systems or containment to reduce accidental spills or evaporation.
- Training is Key: Educate all employees on the risks and correct response actions in emergencies.
For Consumers:
- Select Verified Products: Choose items with certifications indicating low emissions or safe handling of materials during manufacturing.
- Avoid Unnecessary Exposure: When using products with TDI-based polyurethane (like certain foams or adhesives), use in well-ventilated areas or follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Additional details about TDI handling and safety protocols can be found here.
Taking these precautions ensures TDI is used effectively while keeping risks in check. Whether you’re an industry professional or consumer, understanding safety guidelines is essential when dealing with chemicals like TDI.
Environmental Impact of Toluene Diisocyanate
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is a widely used chemical, but its environmental impact cannot be ignored. Improper handling can affect air, soil, and water quality, posing challenges for ecosystems and public health. Understanding its environmental implications is essential for safer usage.
TDI Volatility and Toxic Fume Emissions
One of the main environmental concerns about TDI is its volatile nature. When not properly stored or transported, TDI can release toxic fumes into the air. These emissions often include isocyanate vapors, which are highly reactive and can cause respiratory issues in humans and animals.
- Air Contamination: These fumes can lead to air pollution, particularly in industrial areas. When TDI is exposed to heat or moisture, it can undergo chemical reactions, amplifying fume release.
- Storage Hazards: Inadequate containment systems or damaged containers can result in accidental spills. This allows the chemical to evaporate into the air, causing localized air quality degradation.
- Risks During Transportation: Leaky containers during transit pose significant risks. Any release can impact both the immediate area and the environment along transportation routes.